“昆明滇池面山森林可持续经营国家长期科研基地”于2019年获国家林草局批准,由学术委员会和管理委员会共同管理。学术委员会主任为中国林科院唐守正院士,成员包括国内外知名学者;管理委员会由昆明市海口林场负责建设维护,西南林业大学提供科技支撑。
基地现有工作人员40余名,含黄大年教师团队负责人1人 ,国家林业和草原局教学名师1人,云南省师德标兵1人,10余人入选“兴滇英才支持计划”。
基地支撑人员依托智慧林业教研室,教师人均主持2项国家自然科学基金,已发表含中科院一区的论文百余篇,建设示范区2000余亩,形成学术、管理、科研与示范一体化体系,取得显著生态、经济和社会效益,目标是建设国内领先、国际一流的科研平台。
方向1:森林参数估测与不确定性分析
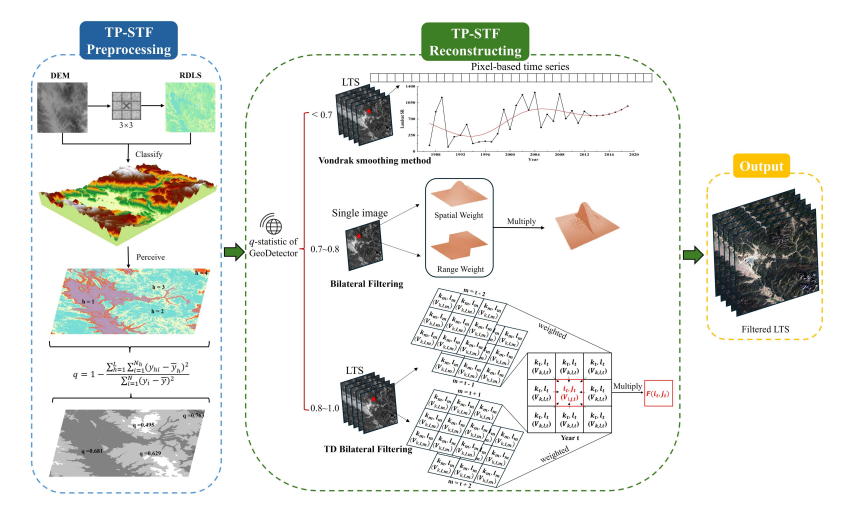
本方向专注于利用遥感技术,结合多源数据,开展森林生物量、碳储量、碳汇的估算研究,重点研究遥感影像与地面数据的融合方法及其应用。通过优化Landsat时间序列数据的滤波方法,提高了森林碳储量的估算精度,开发了基于随机森林和蒙特卡洛方法的森林参数不确定性分析框架。此外,还结合深度学习与多源遥感数据,提出了新的松林参数估测方法,为生态环境保护与森林资源管理提供了理论支持。
代表性成果:
1)Zhang Jialong, Lu Chi, Xu Hui, et al. Estimating aboveground biomass of Pinus densata-dominated forests using Landsat time series and permanent sample plot data. Journal of Forestry Research, 2019, 30(5):1689-1706.
2)Huang Kai , Teng Chenkai , Zhang Jialong , et al. A New Spatiotemporal Filtering Method to Reconstruct Landsat Time-Series for Improving Estimation Accuracy of Forest Aboveground Carbon Stock. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025,18.
3)滕晨凯,肖月瑶,张加龙,和云润,陈朝情. 基于Landsat时间序列数据和ATC滤波算法的高山松碳储量估测. 遥感学报, 2024, 28(11):2927-2942.

方向2:森林领域雷达遥感技术创新与实践应用
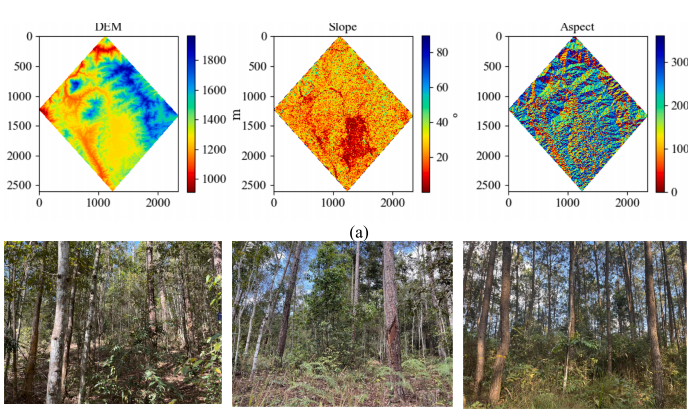
本方向专注于基于三维遥感技术进行森林生物量和碳储量的估测,尤其是在复杂地形条件下的高精度估测技术。提出了利用多源遥感数据和深度学习算法相结合的方法,极大地提高了森林生物量和碳储量的估算精度。开展了基于Lidar数据、SAR数据及光学遥感数据的集成分析,推动了碳储量反演技术的创新和应用,为森林管理和气候变化应对提供了科学依据。
代表性成果:
1)Luo Hongbin, Yue Cairong, Ou Guanglong, et al. A framework for montane forest canopy height estimation via integrating deep learning and multi-source remote sensing data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2025, 138, 104474.
2)Yu Zhibo, Wu Yong, Zhang Ziyu, et al. A precise estimation framework for individual tree AGB of Pinus kesiya var. Langbianensis utilizing point cloud registration Optimization. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2025,140, 104612.
3)Zhao Han, Zhang Tingwei, Ji Yongjie, et al. Uncertainty analysis for forest height inversion using L/P band PolInSAR datasets and RVoG model over kryclan forest site. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2024, 13, 103886.

方向3:森林生态参数精准反演
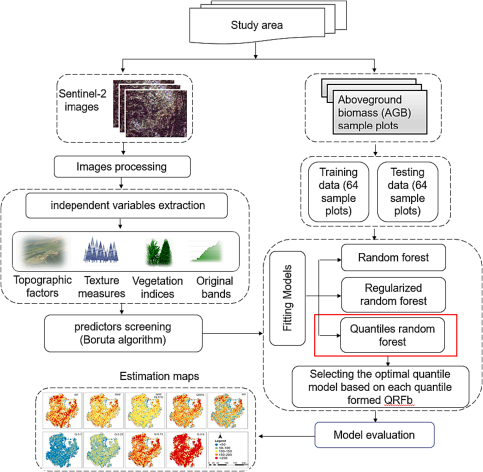
本方向致力于遥感技术在生态环境监测中的应用,特别是通过遥感影像和模型结合,进行森林生物量、树高等关键生态指标的动态监测。利用三维绿度信息与遥感生态指数等指标,优化了森林生态环境质量评估方法,并提出了基于深度学习与多源遥感数据的森林冠层高度估测框架,进一步推动了森林生态监测的技术进步和应用实践。
代表性成果:
1)Hong Zehu, Liu Yun, Xu Weiheng, et al. A new method of three-dimensional green volume retrieval and its applications in urban greenery evaluation. Ecological Indicators, 176:113629, 2025.
2)Xiong Yuan, Xu Weiheng, Lu Ning, et al. Assessment of spatial-temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: A case study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecological Indicators, 125, 107518, 2021.
3) Zhang Xiaoli, Shen Hanwen, Huang Tianbao, et al. Improved random forest algorithms for increasing the accuracy of forest aboveground biomass estimation using Sentinel-2 imagery. Ecological Indicators, 2024, 159, 111752.
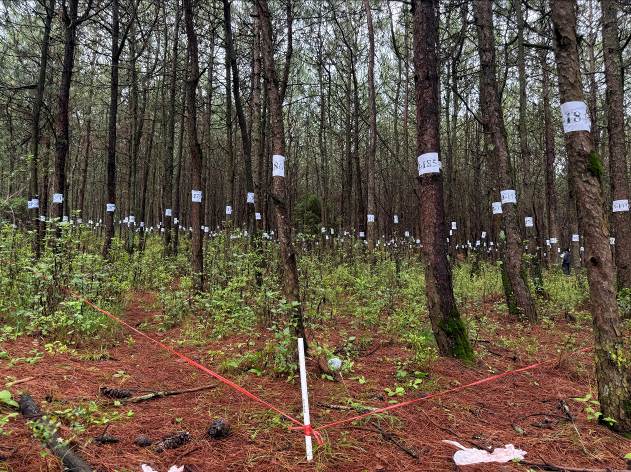

方向4:森林生态系统恢复与质量提升
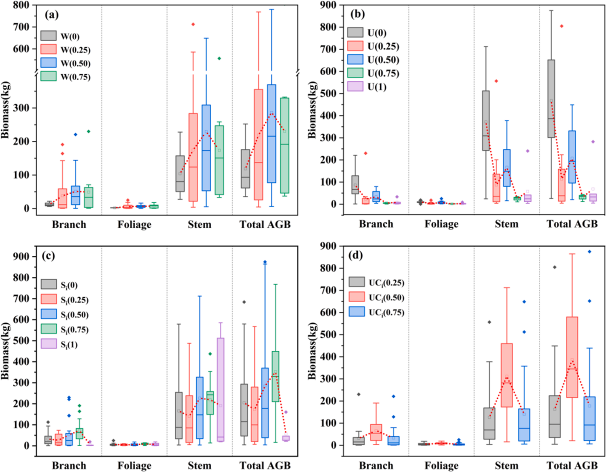
本方向聚焦森林生态系统恢复、经营管理及可持续发展研究:探索退化森林、采伐地等不同场景的恢复技术创新与应用;研究林木空间分布、竞争关系等林分结构要素对碳储量与生物多样性的作用机制,构建多尺度评价方法并提出优化措施;结合二者开发区域适配的综合经营模式,经示范应用获显著成效,为森林生态稳定与可持续利用提供科学支撑。
代表性成果:
1)Li Jing, Huang Xiaobo, Li Shuaifeng, et al. Microbial network complexity and diversity together drive the soil ecosystem multifunctionality of forests during different woodland use intensity in dry and wet season. Forest Ecology and Management, 2023, 542: 12108.
2)Liu Zhi, Zhang Xiaoli, Wu Yong, et al. LiDAR-based individual tree AGB modeling of Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis by incorporating spatial structure. Ecological Indicators, 2024, 169, 112973.
3)Fan Qinling, Xu Hui, Luo Dapeng, et al. Characterising spatial effects of individual tree and component biomass for three typical tree species in Yunnan, China. Ecological Indicators, 2024, 159, 111705.