团队依托云南省森林灾害预警与防控重点实验室组成,围绕西南地区严重危害云南松、华山松、核桃、澳洲坚果等的重要有害生物,研究其致害成灾机制,研发绿色防控关键技术。团队成员中有教授4人、副教授4人、讲师10人,国家林草科技创新计划青年拔尖人才1人,中国科学院“西部之光”人才培养计划“西部青年学者”1人,云南省中青年学术和技术带头人1人,云南省“兴滇英才支持计划” 教学名师1人、青年人才7人,组建有云南省教育厅科技创新团队1个、云南省教育厅博士生导师团队2个。团队近五年主持各级科研项目30余项,获省部级科技奖励3项,发表SCI论文80余篇。

代表性成果
方向1:天敌昆虫控害机制与害虫绿色防控技术研发
以寄生蜂、捕食性蝽、蚂蚁等天敌昆虫为研究对象,研究天敌昆虫控害机制,重点围绕天敌昆虫毒液基因起源进化、天敌昆虫毒液功能基因发掘以及天敌昆虫毒液功能基因应用开展研究。围绕森林及经济林重要害虫,重点研发基因工程微生物杀虫制剂、RNAi纳米农药、转基因抗虫植物、新型化合物杀虫制剂等绿色防控技术。近五年,主持国家及省部级科研项目12项,其中国家自然科学基金项目3项、省部级人才项目4项、云南省应用基础研究重点项目1项、云南省农业基础研究联合专项重点项目1项、云南省大观实验室项目1项;发表SCI论文30余篇,获授权国家发明专利2件。
在研项目
1. 国家自然科学基金项目, 黄带犀猎蝽毒液中胃毒型杀草地贪夜蛾化合物的发现及其作用机制研究
2. 云南大观实验室项目, 夜蛾黑卵蜂适应替代寄主的分子进化及其控害机制研究
3. 云南省教育厅科技创新团队项目,天敌昆虫毒液资源挖掘及其应用研究
4. 云南省“兴滇英才计划”青年拔尖人才专项后续项目, 捕食性蝽毒液源抗虫ICK多肽发掘利用研究
5. 云南省基础研究计划基金项目,黄带犀猎蝽毒液triabin杀猎物血细胞生理功能的发现及验证研究
代表性成果:
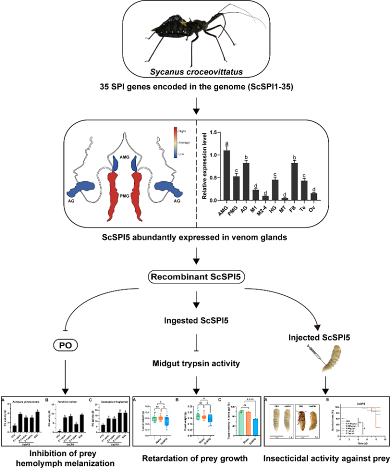
1. Liang W, Li M, Chen F, Wang Y, Wang K, Wu C, Zhu J*, 2025. A venom serpin from the assassin bug Sycanus croceovittatus exhibiting inhibitory effects on melanization, development, and insecticidal activity towards its prey. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 209: 106322.
2. Wang K, Wu G, Ma Q, Yang L, Wu C, Zhu J*, 2025. Unraveling the venom constituents of the endoparasitoid Aphidius gifuensis with an emphasis on the discovery of a novel insecticidal peptide. Pest Management Science, 81(3): 1603-1614.
3. Yang L, Zhu J*, 2025. Venom apparatus, composition, function, evolution, and potential applications of caterpillar venom. Entomologia Generalis, 45(3):? 635-650.
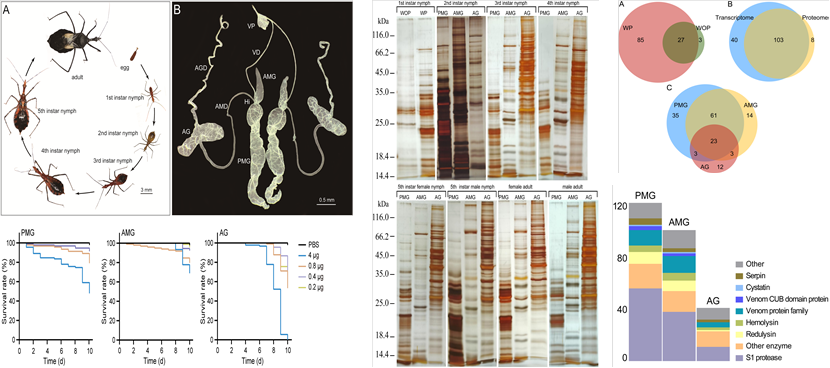
4. Wu C, Li L, Wang Y, Wei S, Zhu J*, 2023. Morphological, functional, compositional and transcriptional constraints shape the distinct venom profiles of the assassin bug Sycanus croceovittatus. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 7: 126162.
5. Wang Y, Luo Y, Ge Y, Liu S, Liang W, Wu C, Wei S, Zhu J*, 2024. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the predatory stink bug Arma custos. Scientific Data, 11(1): 417.
6. 朱家颖, 张祖兵, 王大伟. 一种辣木瑙螟性信息素引诱剂. ZL202111566019.9 (授权公告日: 2023.4.18)
7. 朱家颖, 张祖兵, 柯慧琦, 王大伟. 一种基于辣木叶片挥发物质的辣木瑙螟引诱剂. ZL202111591644.9 (授权公告日: 2023.5.2)
方向2:森林害虫多模态信息整合与综合治理研究
以松切梢小蠹为研究对象,以切梢小蠹两性生殖的化学和物理信号开展为切入点,综合应用繁殖生物学、化学生态学、生物振动学、视行为学等技术,重点解析切梢小蠹的寄主与非寄主植物气味、聚集信息素、表皮碳氢化合物、求偶声信号的时域空域及行为背景间的共性和特性,结合正选婚配和资源生态位,整合化-声-视共性信息,通过诱杀、干扰、趋避等多途径构建松切梢小蠹绿色无公害控虫体系,以期精准调控与可持续治理松切梢小蠹危害。

在研项目
1. 国家自然科学基金,云南切梢小蠹肠道关键功能菌群及其信息操控
2. 国家自然科学基金,雌雄异株榕果-传粉榕小蜂互惠系统的“共生弹性”对干旱胁迫的响应
3. 国家自然科学基金,榕树-榕小蜂繁殖共生系统对热带海拔梯度的生态响应与级联
2.国家自然科学基金,榕-蜂共生系统防御蚂蚁捕食的机制及其生态学效应
3.云南省兴滇英才支持计划专项,传粉模式对榕属植物及其传粉小蜂互作稳定性的影响
4.云南省基础研究计划农业联合专项,共生菌对云南切梢小蠹生长发育和性发育调控机制的研究
5.云南省人力资源和社会保障厅,2025年永仁县维的乡板栗产业专家基层科研工作站
代表性成果:
1. Liao Z, Shen X, Zhang J, Zhu M, Deng Z, Liu F, Huang Z.Y, Zhang Y*, 2025. Vegetation coverage and land imperviousness in urban area jointly affect hymenopteran pollinator diversity and spatial pattern. Ecological Indicators, 178: 114116.
2. Xie H, Shi Y, Zhang S, Zhu Y, Shao S, Zhang Y, Yang P*, Li Z*, 2025. Fine structure and optical features of the compound eyes of adult female Ceratosolen gravelyi (Hymenoptera: Agaonidae). Insects, 16(7): 682.
3. Xie H, Yuan H, Wang Y, Tang X, Yang M, Zheng L*, Li, Z*, 2025. Compound eye structure and phototactic dimorphism in the Yunnan pine shoot beetle, Tomicus yunnanensis (Coleoptera: Scolytinae). Biology, 14: 1032.
4. Liu J, Zhang M, Qian L, Wang Z*, Li Z*. 2025. Electrophysiology and behavior of Tomicus yunnanensis to Pinus yunnanensis volatile organic compounds across infestation stages in southwest China. Forests, 16: 1178.
5. Chen C, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Li Z, Zhang Y*, 2025. Feeding preferences, growth patterns and reproductive characteristics of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) indicate the potential of Ficus tree as new host plant. Agriculture, 15: 1187.
6. Guan Y, Zhang Y, Li Z, Wang Y, Chen C, Yang X., Gao J, Miao B, Peng Y*, Zhang Y*, 2025. The impact of pollinating fig wasps’ entry on fig development and the hormonal regulation of sex differentiation in Ficus hispida. Forests, 16: 286.
7. Yang X, Guan Y, Chen C, Zhang Y, Yuan Y, Tang T, Li Z, Zhang Y*, 2024. The effect of Ficus semicordata fig quality on the sex ratio of its pollinating wasp Ceratosolen gravelyi. Diversity, 16: 298.
8. Zhang Y, Guan Y, Li Z, Wang Y, Chen C, Yang X, Zhang Y*, 2025. The entry of pollinating fig wasps plays a pivotal role in the developmental phase and metabolic expression changes in Ficus hookeriana figs. Forests, 16: 165.
9. 谢华, 杨培, 李宗波*, 2024. 鸡嗉子榕传粉榕小蜂表皮碳氢化合物的性二型及季节变化. 生物多样性, 32: 24001.
方向3:林业害虫寄主和生境适应机制
重点关注西南地区造林树种和经济林树种上发生和为害严重的林业害虫,研究它们与微生物、寄主和非寄主植物的互作,探究害虫在多变化学生境中的适应机制。研究团队在切梢小蠹、云南锦斑蛾、冷杉梢斑螟、管纹艳虎天牛等林业害虫关键化感基因挖掘和致害成灾机制方面取得显著成果,在Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology、Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology、Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry、昆虫学报等国内外学术期刊上发表论文90余篇,其中第一或通讯作者发表SCI论文47篇,中科院一区TOP论文9篇;主持国家自然科学基金项目3项,云南省“兴滇英才支持计划”青年人才项目1项,云南省基础研究专项重点、面上和青年项目各1项,云南省农业联合面上项目1项;刘乃勇教授入选云南省“兴滇英才支持计划”青年人才,获第十届国际亚太化学生态会会议(APACE)青年科学家奖,现任中国昆虫学会第十一届理事会化学生态学专业委员会委员。
 ?
?

在研项目:
1. 国家自然科学基金项目,云南锦斑蛾跗节高表达CSP基因对两种广谱杀虫剂胁迫的响应及其功能研究
代表性成果:
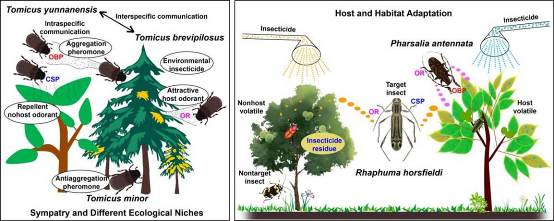
1. Li SL, Li FP, Yang ZX, Zhao YJ, Li ZQ*, Liu NY*, 2025. Functional characterization of odorant binding proteins in Pharsalia antennata provides insights into diverse binding properties and the importance of C-terminal residues. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 214: 106566.
2. Lu YY, Li SL, Li FP, Long ZH, Lu TT, Liu NY*, 2025. Comparative analyses of odorant binding protein orthologues in three sympatric Tomicus bark beetles provide insights into functional differentiation of OBPs to ecologically relevant odorants and insecticides. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 290: 138862.
3. Pu LM, Wang PF, Lu YY, Yang AJ, Liu LL*, Liu NY*, 2025. Functional characterization of chemosensory proteins in three sympatric Tomicus bark beetles feeding on Pinus yunnanensis: Implication for the conservation and divergence of ligand-binding profiles. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 210: 106371.
4. Liang YL, Li SS, Yin NN, Li SL, Lu YY, Liu NY*, 2024. Functional characterization of four antenna-enriched odorant binding proteins in Rhaphuma horsfieldi reveals the importance of RhorOBP1 in odorant recognition and insecticide resistance. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 206: 106210.
5. Yao YJ, Yin NN, Pu LM, Yang AJ, Liu NY*, 2024. Three chemosensory proteins enriched in antennae and tarsi of Rhaphuma horsfieldi differentially contribute to the binding of insecticides. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 199: 105797.
6. Yin NN, Yao YJ, Liang YL, Wang ZQ, Li YH, Liu NY*, 2023. Functional characterization of four antenna-biased chemosensory proteins in Dioryctria abietella reveals a broadly tuned olfactory DabiCSP1 and its key residues in ligand-binding. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 197: 105678.
7. Yin NN, Yang AJ, Wu C, Xiao HY, Guo YR, Liu NY*, 2022. Genome-wide analysis of odorant-binding proteins in Papilio xuthus with focus on the perception of two PxutGOBPs to host odorants and insecticides. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 70(35): 10747-10761.
8. Li JL, Yuan TT, Cai XM, Luo ZX, Bian L, Xiu CL, Fu NX, Chen ZM, Liu NY*, Li ZQ*, 2022. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated tyrosine hydroxylase knockout in Ectropis grisescens results in defects in the melanization of the integument, excluding sclerotized appendages. Entomologia Generalis, 42(6): 997-1004.
方向4:林业病原物致害成灾机制与绿色防控
聚焦林业病原物致害成灾机制以及绿色防控研究。重点关注云南林业病原物入侵、定殖、扩展的路径;进而解析气候—寄主—微生物互作网络,阐明病害流行阈值与暴发的生态驱动机制;在此基础上建立早期预警与抗性育种平台,实现生防微生物应用、基因编辑和森林结构调控;最终集成生物防治、诱抗剂与无人机精准施药,形成替代化学农药的绿色防控技术体系,为云南省林业病害可持续治理提供全链条解决方案。近五年来,研究团队共主持省部级以上项目15项,其中,国家级项目5项,发表SCI源期刊论文15篇,出版学术专著5部,培养硕士研究生25人、博士研究生5人。

在研项目:
1. 云南省农业联合基金面上项目:苹果根际合成菌群对病原性再植障碍的缓解效应及机理研究
2. 云南省应用基础研究青年基金项目,石榴灰斑病绿色防控体系构建
3. 云南省农业联合基金面上项目,daf-16信号通路在秀丽隐杆线虫响应胶胞炭疽菌中的作用及对植物抗病性研究的借鉴意义
4. 国家自然科学基金,墨兰菌根真菌多样性与根腐病发生的抑病机理研究
5. 松材线虫病预防与控制技术国家林业和草原局重点实验室:淡紫拟青霉在松材线虫防治中的应用研究
代表性成果:
1. Wu Z, Chen J, Chen J, Yang Y, Zhou A, Wu J*, 2025. The relationship between pomegranate root collar rot and the diversity of fungal communities in its rhizosphere. Frontiers in Microbiology, 16: 1573724.
2. Liu H, Cheng H, Xu S, Zhang D, Wu J, Li Z, Fu B, Liu L*, 2025. Genetic diversity and growth-promoting functions of endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria in apple. Plants, 14(8): 1235.
3. Peng R, Zhou A, Chen J, Wen M, Wang F, Wu J*, 2025. Antifungal activity of bacillus velezensis hy13 against anthracnose disease of buxus bodinieri caused by Colletotrichum fructicola. Biological Control, 208: 105845.
4. Ma A, Xu Y, Feng H, Du Y, Liu H, Yang S, Chen J, Hao X*, 2025. Identification of avocado fruit disease caused by Diaporthe phaseolorum and Colletotrichum fructicola in China. Journal of Fungi, 11(8): 547.
5. Chen J, Jiao N, Ran Y, Wu Z, Pan J, Lu X, Hao X*, 2024. Assessing effect of Trichoderma asperellum T16 on management of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Industrial Crops and Products, 215: 118628.
6. Chen J, Hong K, Ma L, Hao X*. 2024.Effect of time series on the degradation of lignin by Trametes gibbosa: Products and pathways. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 281: 136236.
7. 易杏盈, 肖月, 张东华*, 2024. 尖孢镰刀菌对秀丽隐杆线虫生物学特性及表达转录组的影响. 华南农业大学学报, 45(3): 381-389
8. 朱幼娇, 陈健鑫, 吴峰婧琳, 彭睿琦, 温名佳, 马焕成, 伍建榕*, 2025. 耐盐芽孢杆菌对油茶炭疽病的抑制作用及机制研究. 华南农业大学学报, 46(5): 659-668.
9. 伍建榕, 油茶病害与防控机制研究. 科学出版社. 2025-03. ISBN:9787030815729.
10. 西南林业大学教学成果一等奖:“油茶卫士”-科学防治炭疽病,助力油茶促振兴;第四届全国大学生植物保护专业能力大赛:团体二等奖;1特等奖;5个二等奖;3个三等奖.
方向5:林业有害生物遥感监测与预警
以切梢小蠹、松叶蜂、红脂大小蠹等林业有害生物为研究对象,使用遥感卫星、多光谱无人机、高光谱无人机以及热红外无人机等技术开展相关研究,重点聚焦于有害生物危害早期的精准识别与发生动态预警。在监测方面,通过多源遥感信息解析寄主植物的胁迫响应特征,实现对有害生物侵染的早期诊断;在预警方面,综合运用生态学、景观生态学原理以及风险分析、适生区建模等技术,模拟与预测有害生物的扩散趋势与潜在分布,旨在构建“早期监测-动态预警”一体化技术体系。目前,研究团队已在小蠹虫和叶蜂类害虫的遥感识别模型及其时空扩散规律等方面取得进展,相关成果在Forest Ecology and Management、Remote Sensing等领域知名期刊上发表论文14篇,并获授权发明专利1项、计算机软件著作权1项。在研科研项目6项,其中国家自然科学地区基金1项,云南省青年基金1项。
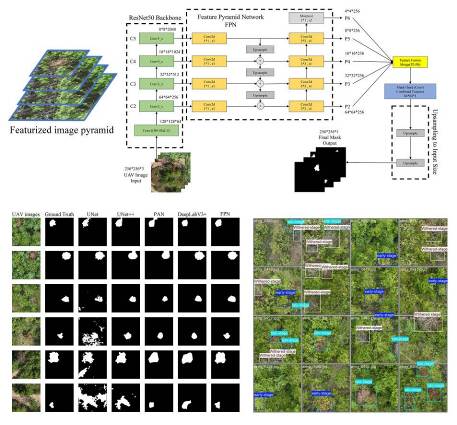
在研项目:
1.国家自然基金:森林扰动景观对切梢小蠹和松墨天牛危害云南松的影响机制研究
2.云南省青年基金:基于多光谱无人机切梢小蠹早期危害木识别研究
3.北京林业大学森林保护重点实验室基金:基于高光谱无人机的切梢小蠹早期危害监测研究
4.西南林业大学林学院重点实验室基金:基于Sentinel卫星的切梢小蠹早期危害监测研究
5.横向课题:南华县林木钻蛀性害虫系统调查
6.横向课题:姚安县林木钻蛀性害虫系统调查
代表性成果:
1. Zhan Z, Yu L, Li Z, Ren L, Gao B, Wang L, Luo Y*, 2020. Combining GF-2 and Sentinel- 2 images to tree mortality caused by red turpentine beetle during the early outbreak stage in North China. Forests, 11(2): 172.
2. Zhan Z, Yu L, Ren L, Liu Y, Lu Z, Luo Y*, 2022. Infestation patterns of incipient red turpentine beetle populations in fire-affected, logged and undisturbed forest stands of northern China. Forest Ecology and Management, 521: 120424.
3. Zhan Z, Yu L, Ren L, Gao B, Li H, Wang L, Luo Y*, 2023. The association between stand and landscape level factors and red turpentine beetle damage in different infestation stages. Forest Ecology and Management, 531: 120790.
4. Wang L, Gao Y, Liu Y, Zhong L, Wang S, Ma Y, Zhan Z*, 2025. Monitoring pine shoot beetle damage using UAV imagery and deep learning semantic segmentation under different forest backgrounds. Forests, 16(4): 668.
5. 詹钟易, 王雷光, 杨松, 王丽霞, 王世春云.国家知识产权局, 基于数据分类的害虫识别系统及方法, 2025年7月15日, 专利号:ZL202411562216.7
6. 詹钟易, 杨松, 王丽霞. YOLOv7驱动的切梢小蠹虫害监测和预警系统V1.0, 中华人民共和国国家版权局, 2024年10月17日, 登记号:2024SR1552015.